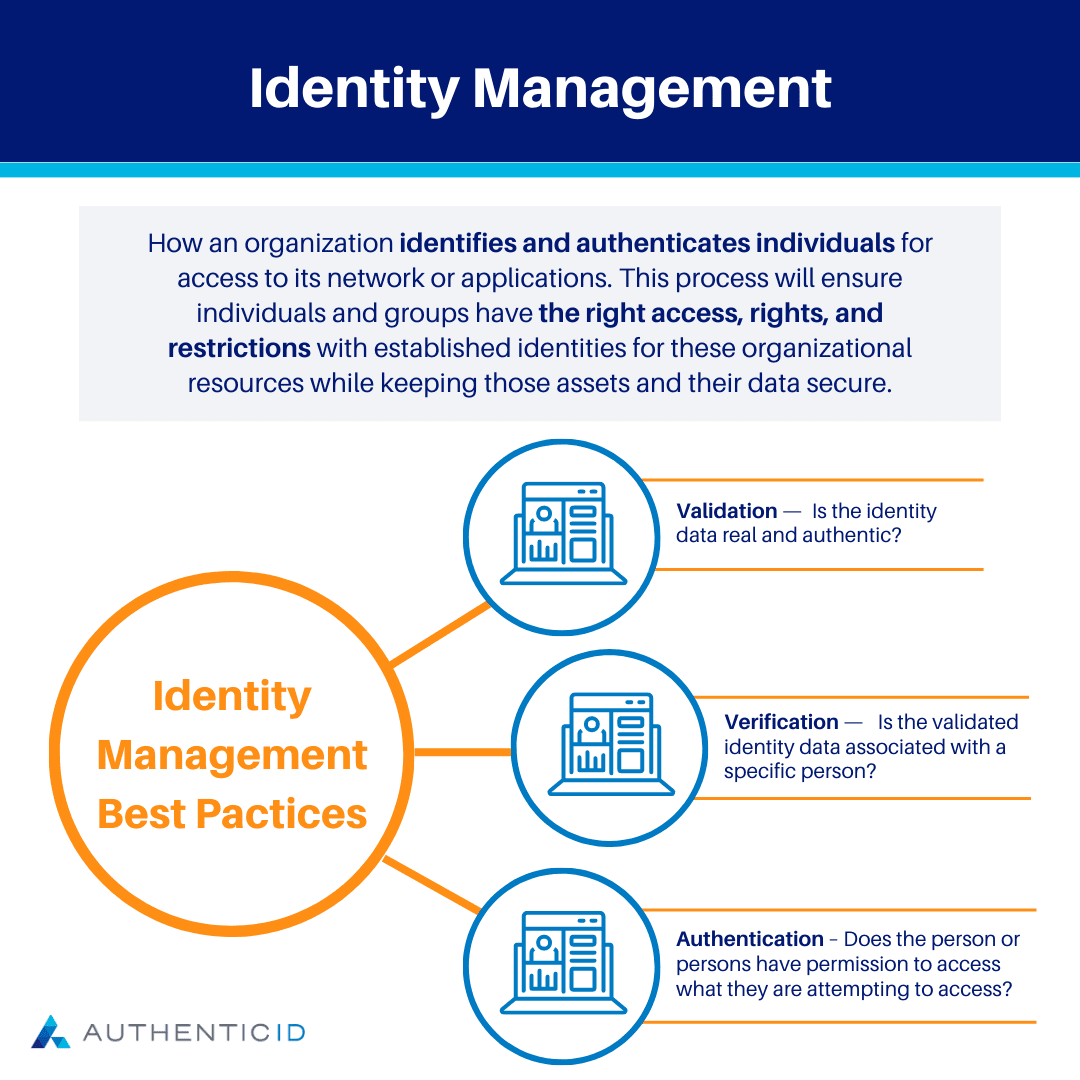
Identity management is how an organization identifies and authenticates individuals for access to its network or applications. This process will ensure individuals and groups have the right access, rights, and restrictions with established identities for these organizational resources while keeping those assets and their data secure.
Identity management systems include software, hardware, and procedures used to identify and authorize a person or persons that need access to applications, systems, networks, or physical locations. This is done by first ensuring that the right person or persons are identified, and then verifying that those persons are authorized to access the item in question.
Identity Management Examples
There are a number of identity management systems available today, but at their most basic level, they all perform a few key functions:
- Validation – Is the identity data real and authentic?
- Verification – Is the validated identity data associated with a specific person?
- Authentication – Does the person or persons have permission to access what they are attempting to access?
Identity management systems use these key functions together in order to gain a better understanding of whether or not the person or persons are who they say they are, and if so, whether they can access what they are attempting to access.
One basic example of this would be if a person were attempting to gain access to your banking information using a fake ID. Let’s imagine that the perpetrator uses a fake driver’s license with their own picture, but it has your name and information on the license. The ID appears to verify the fact that this person is you, and you are obviously authenticated to access your own account. However, the ID itself is not valid because it is not real and authentic. Therefore, no access should be granted in this scenario.
A driver’s license is just one of many examples of identity data. Other examples may include biometric data (fingerprints, facial recognition, selfies, etc.), documents (passports or government-issued ID), challenge questions, or even behavioral signals. Depending on the application and levels of risk, organizations may use a variety of these methods within their identity management process.
Identity and Access Management Strategy
Organizations of all sizes need identity and access management (IAM) solutions to make sure that only authorized people have access to the systems, information, and resources they need to do their jobs. Unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security problems can all be avoided with the help of an efficient IAM approach.
There are several important steps to developing an IAM strategy. The first step is to thoroughly evaluate the IAM practices that are already being used by your company. This can assist you in finding any holes or weak points in your current system as well as potential improvement areas.
The next step is to create explicit policies and processes for controlling user identities and access rights. For enhanced protection, this may also entail creating user accounts, defining roles and permissions, and putting multi-factor authentication (MFA) into place.
In order to make sure that access is being utilized properly, it is also important to have a procedure in place for monitoring and reviewing it. This can entail setting up automated alerts to inform you of any questionable activity, as well as routinely examining user access logs.
Implementing appropriate security measures to guard against data breaches and other security threats is another critical component of an IAM strategy. This could involve building firewalls and other security measures to block illegal access, as well as deploying encryption to safeguard data while it is in transit and at rest.
Finally, it’s important to have a strategy in place for controlling and revoking access if employees leave the company or take on new responsibilities. By doing this, it is made possible to guarantee that former employees no longer have access to corporate assets and that current employees only have access to the systems and information they require to carry out their jobs.
Any corporation that wants to safeguard its resources, data, and systems must have a strong IAM strategy. You can ensure that only authorized users have access to your systems and that your organization is safe from data breaches and other security threats by conducting a thorough assessment of your current IAM practices, establishing clear policies and procedures, monitoring access, and putting in place suitable security measures.
Why do we need identity management?
Identity management is crucial because it ensures that only individuals with the proper authorization can access the systems, information, and resources required to carry out their job obligations. Additionally, it aids in preventing security events like data leaks and illegal access.
Organizations of all sizes rely on a variety of tools and technologies to function and compete in today’s digital world. These resources might include private company information, client data, and other priceless assets. Controlling who has access to these resources can be challenging without effective identity management, which puts the organization at risk for security attacks, data breaches, and other possible harm.
Identity management additionally aids in ensuring compliance with laws and industry standards pertaining to data protection and privacy. Organizations may prove to regulators, consumers, and other stakeholders that they are taking the necessary precautions to secure sensitive information by implementing effective identity management processes.
Identity Management Best Practices
For enterprises of all sizes trying to protect their systems, data, and resources, identity management best practices are essential. By putting these best practices into effect, companies may guard against unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security concerns while ensuring that only authorized people have access to the resources they need to do their jobs.
When creating an identity management strategy, keep the following essential best practices in mind:
- Analyze your present identity management procedures in-depth: This can assist you in finding any holes or weak points in your current system as well as potential improvement areas.
- Create policies and processes that are clear: This guarantees that only authorized users have access to the systems and resources they require, create user accounts, define roles and permissions, and implement multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Regularly analyze user access logs and keep an eye out for any unusual activity by monitoring and reviewing access.
- Use encryption to safeguard data both in transit and at rest, and put firewalls and other security measures in place to thwart illegal access.
- Have a process in place for controlling and rescinding access as needed as people depart the company or take on new responsibilities. By doing this, it is possible to guarantee that former employees no longer have access to corporate assets and that current employees only have access to the systems and information they require to carry out their jobs.
- Maintain and update your identity management system on a regular basis: To defend against new attacks, keep your identity management system up to date with the most recent security patches and software updates.
- Employees should receive training and resources: Teach your staff the best practices for identity management, such as how to set secure passwords and how to spot and report questionable activities.
By adhering to these best practices, businesses can make sure that their identity management systems are efficient at safeguarding their resources, data, and systems while also preserving the confidence of their clients and other stakeholders.
