Know Your Customer (KYC) is a set of standards and regulations used by financial institutions to make sure that they’re doing business with a legitimate, law-abiding person or entity.
When you open a bank account, apply for a credit card, or take out a loan, the financial institution you do business with will ask you to provide some personal information—namely, your Social Security number and proof of your identity (AKA your KYC documents). This is because the institution needs to be able to identify you before it starts doing business with you. The same goes for businesses that open bank accounts or apply for loans from financial institutions.
KYC compliance is important both for keeping businesses safe from fraud and for helping them comply with laws and regulations.
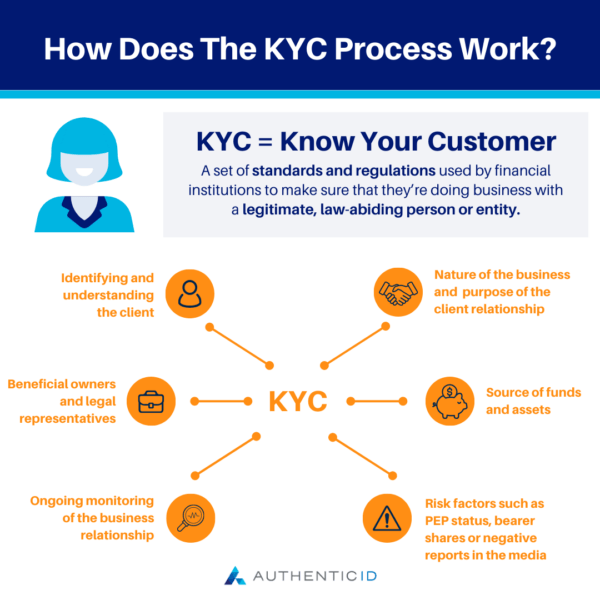
How Does the KYC Process Work?
Know Your Customer is a way for companies to ensure their customers are who they say they are, and that the customer isn’t involved in criminal or terrorist activity.
When a business starts working with a new customer, it will need to collect certain information from that customer. The exact information varies by industry and business, but often includes things like the customer’s name, address, date of birth, and contact information.
If a company is not able to verify this information with a third party—for example, if all the addresses provided by a customer give a “no such address” error on Google Maps—it may have to take additional steps to ensure the identity of the customer before it can do business with them.
A company’s KYC process typically involves:
- Collecting personal information from customers (KYC documents)
- Checking that information against a database of known fraudulent activity, people, or organizations (KYC verification)
- Maintaining records of the verification process (KYC compliance)
The steps involved in KYC are typically part of a larger set of processes for onboarding customers.
What Industries Use KYC?
KYC is relevant for financial services companies, energy companies, and pharmaceutical companies to name a few.
In the financial services industry, KYC protects against identity theft and fraud for both individuals and businesses. For example, a bank might use some form of KYC to verify a customer’s identity before opening an account for them or issuing them a credit card.
In the energy industry, KYC is used to validate whether or not potential partners can meet the needs of their business. For example, if an oil company were looking to partner with a supplier of vehicles and services, they would likely want to run KYC on that company for assurance that it had the capacity and credentials needed for that partnership.
In the pharmaceutical industry, KYC is used by regulatory agencies and law enforcement officials to ensure that companies comply with standards around protecting consumers’ health interests. For instance, the Food and Drug Administration uses KYC to verify which companies are eligible to do business with pharmaceutical companies or are approved to manufacture drugs.

What Regulations Are Tied to KYC?
KYC is required by regulatory bodies such as the FDIC and the Federal Reserve.
There are several KYC regulations, but here are the primary ones:
- The Bank Secrecy Act of 1970
- USA Patriot Act of 2001
- Money Laundering Control Act of 1986
- Anti-Money Laundering Act of 1992
- Intelligence Reform and Terrorism Prevention Act of 2004
- Uniting and Strengthening America by Providing Appropriate Tools Required to Intercept and Obstruct Terrorism (USA PATRIOT) Act of 2001
- Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA)
Benefits and Advantages to KYC Compliance
It’s the new wave of customer service: Know Your Customer.
Organizations initiate KYC processes to ensure that customers are who they say they are and are not using fraudulent credit cards, bank accounts, or engaging in money laundering.
From a financial institution’s perspective, KYC is essential to preventing fraud, complying with federal regulations and anti-money laundering laws, and implementing customer due diligence practices.
Further, KYC brings many benefits: It protects against money laundering (AML) and fraud, enables you to build better relationships with your customers, and helps you comply with applicable laws.
Companies have also learned that they can’t afford to treat customers as faceless entities or numbers on a screen anymore. They recognize that their success depends on understanding and respecting their clients’ needs.
As more organizations focus on KYC compliance, they see the financial benefits it brings. A company with a robust and well-defined customer profile knows precisely what its target market wants. In addition, it saves money by avoiding investing in products and services that don’t appeal to its core audience. This highly focused approach also helps companies deliver better services to their customers, who feel respected and understood.
With a comprehensive customer profile comes a better understanding of improving customer retention and loyalty. Because KYC focuses on understanding the customer’s behavior and motivations, companies can provide better support when issues arise or improve existing products and services.
What Are Some of the Latest KYC Methods?
KYC is usually a one-time process involving manual entry of data and identity verification that takes place at account opening. Traditional KYC methods involve a lot of documentation and manual entry into bank systems, which requires staff time and money.
Advanced technologies like blockchain, biometrics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning are helping banks evolve their KYC practices beyond simply verifying a customer’s identity. These systems can detect high-risk customers or transactions in real-time, streamlining the KYC process while assisting banks to safeguard against fraud and illicit activity.
KYC methods include:
- Matching the client’s identity information with a third-party database.
- Running a social media check to see if the person is whom they claim to be.
- Checking the client’s picture against their ID.
- Conducting interviews with clients over the phone or in-person to verify their ID, financial background, and other essential details.
Advanced cost-cutting methods integrate Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning to identify patterns in transactions and detect fraudulent activity. It involves setting parameters for behavioral patterns within the customer’s transaction history. Using this type of software can determine if there is any unusual behavior, such as suspicious transactions or money laundering activity, based on these behavioral patterns.
To automate this process, some financial institutions are turning to Artificial Intelligence (AI) platforms that enable companies to self-manage their KYC checks. These platforms are designed to facilitate automated checks on existing customers and new ones. In addition, automating these activities enables increased efficiency so that financial institutions can save money during the onboarding.

