An important cybersecurity practice that keeps your online accounts safe, Reauthentication is widely used across the web today and provides various benefits that you may not even be aware of.
What Is Reauthentication?
Reauthentication is a cybersecurity concept that refers to the process of requiring users to offer additional verification or authentication credentials to regain their access to a system, application, or account that they have already been logged into.
Requiring users to provide their credentials even after they’ve been authenticated and using the account for some time is implemented as an extra layer of protection. This ensures the user’s identity is being continuously validated, as opposed to providing their login credentials one time and then gaining lifetime access thereafter.
Reauthentication is especially useful for sensitive or high-risk actions or applications within a system. All in all, it is used to add an extra barrier to potential hackers who may have gained access to a device, system, or account through stolen credentials, hacking, or other methods.
How Does Reauthentication Work?
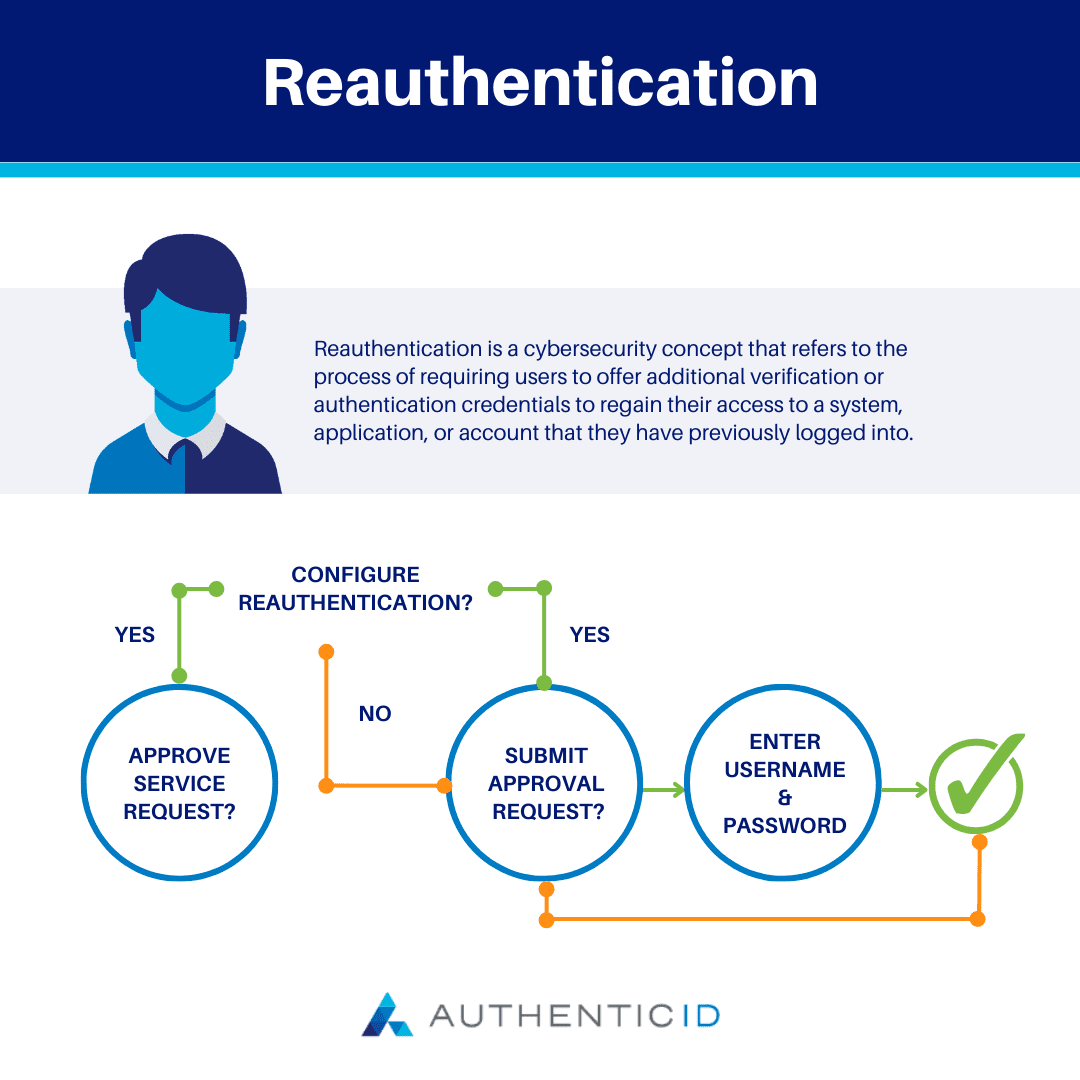
Reauthentication is a straightforward concept. The online account, platform, or system is set up to prompt users to re-enter their credentials after a certain amount of time.
As a user, you must provide your login credentials for each subsequent request to verify your identity and regain access to the system. This may also include additional security measures like Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), Biometric Verification, or answering security questions.
Here are the general steps that are taken during Reauthentication:
1. Initial Authentication: The user first logs into a system or application, providing their authentication credentials (often a username and password).
2. Session Established: After successful authentication, the session is established between the user and the system, and users can access all resources and tasks within the platform.
3. Reauthentication Trigger: Based on the unique policies of the specific system, users will be prompted to reauthenticate at a certain point in their session. The trigger may be accessing sensitive information, performing high-risk tasks, or after a period of inactivity.
4. Reauthenticating Credentials: Following the trigger, the user will need to provide their authentication credentials to verify their identity.
5. Verification: Using the provided credentials, the system will verify the user’s identity with what is stored in the system, then grant them access to continue using the platform uninterrupted until the next trigger.
The Benefits of Reauthentication
As you’ve seen so far, reauthentication is used as an extra layer of security on top of the other methods a system may use. The goal is to prevent unauthorized users from accessing an account, device, or system that already has an active login session, so here are some of the most important benefits that Reauthentication offers.
- Enhanced Security
The largest benefit that Reauthentication provides is enhanced security to prevent unauthorized access to a system or application. Through Reauthentication, users are periodically required to verify their identity, which helps organizations ensure that only authorized users are granted access to their systems. - Better Risk Mitigation
Another major benefit that organizations find with Reauthentication policies is that it can help them reduce the risk of compromised accounts or data breaches. Again, Reauthentication is especially effective for situations that are more high risk like performing a big financial transaction or accessing sensitive information. So, Reauthentication can help prevent fraudulent and unauthorized activities.
Some Reauthentication systems may even be able to monitor users’ account activity and flag suspicious behaviors–like unusual login times or locations. In these instances, Reauthentication can be triggered to validate the user’s identity. In this way, Reauthentication helps with real-time threat detection. If the user fails to present the correct credentials, it could be a sign that the account has been compromised. - Customizable
Many organizations like to use Reauthentication because the policies can be customized and tailored to fit their unique security needs. For instance, they can set up various Reauthentication triggers in their systems based on user roles, types of tasks, or the sensitivity of the data or information being accessed. - Compliance Requirements
It’s important to point out that Reauthentication can also help organizations meet regulatory standards and data protection laws. Most organizations are required to implement strong security measures to safeguard customer data. So, Reauthentication is useful for meeting such compliance requirements by demonstrating their efforts to protect user data and maintain security for the entire system. - Strengthening MFA
Organizations can also use Reauthentication as a way to strengthen their Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) practices by adding an extra layer of security. During Reauthentication, users may need to provide additional authentication credentials outside of their password or username like a code from a mobile app, or a security question to regain access to the system.
Reauthentication Use Cases
Reauthentication can be used across a variety of industries, so here are some of the most common use cases where you’ll see Reauthentication implemented.
- Online Banking: Reauthentication is widely used in the financial services industry like with online banking to prevent unauthorized access to accounts and sensitive data. Users may need to reauthenticate before accessing account details, making transactions, changing settings, or accessing account statements.
- E-commerce: Online storefronts can require users to reauthenticate their accounts when trying to make a larger purchase or change account details. This can prevent unauthorized access to payment methods.
- Healthcare: Reauthentication in the healthcare industry can help protect sensitive patient information, ensuring only authorized parties are privy to their data
- Remote Work: As the remote work trend remains, Reauthentication can be a way for employees to securely access company networks and resources from various off-premise devices and locations. To maintain their secure connection, employees can periodically reauthenticate their credentials.
- Cloud Services: Providers can implement Reauthentication to provide secure remote access to virtual databases and other cloud-based resources.
